
What is the life cycle of a climate project?
What is the life cycle of a climate project?
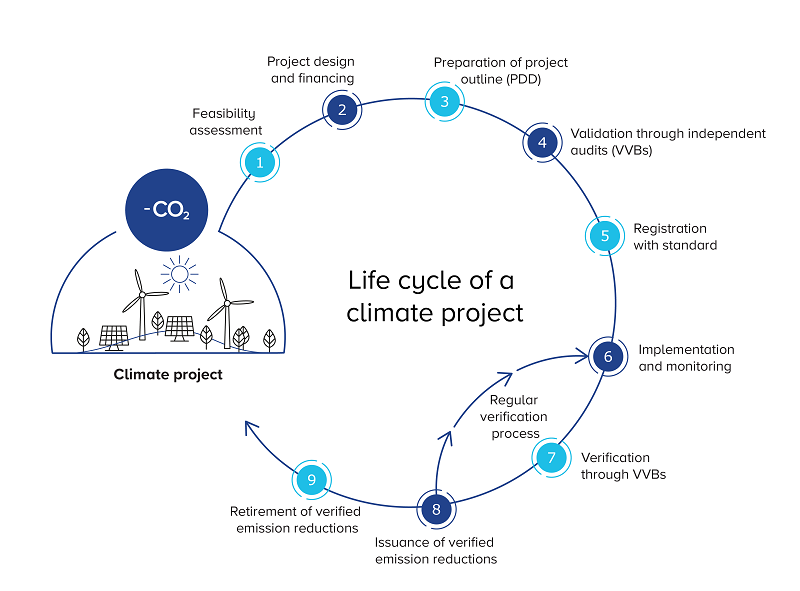
Project planning phase (1-3)
A climate project has a defined life cycle. In the first two steps, the project developer reviews the general feasibility of the project, the project design and the financing. Then, the so-called Project Design Document (PDD) is prepared, which contains all the basic information about the project, such as the project objective, the location, when the project is to be implemented, and the project duration.
Validation (4)
In this phase, independent auditors examine the PDD and the information it contains. This phase often also involves field visits with on-site interviews and analyses. Auditors are accredited, impartial assessors who have to be approved as a validation and verification body (VVB) by the standards body. TÜV Nord/Süd, S&A Carbon LLC., and SCS Global Services are just some examples of validation and verification bodies.
Registration (5)
Once validated, the project can be registered with a standard such as the Verified Carbon Standard or the Gold Standard.
More information about project standards.
Monitoring (6)
After the climate project has been registered, the monitoring phase begins. Here, the project developers monitor and document the data of the project activities and progress. The duration of the monitoring phase varies from project to project, it can cover two years, but documentation over five or seven years is also possible.
Verification (7)
At the end of each monitoring phase, a validation and verification body checks and assesses whether the values and project activities stated in the monitoring report are correct and verifies them. As with validation, visits to the project site are often part of the verification process.
Issuance of verified emission reductions (8)
Once verified, the emission reductions that were confirmed in the verification phase can be issued ex-post as as verified emission reductions. They thus represent the emission savings that actually took place in the past period, which can be one to five years.
The steps of monitoring, project verification and issuance of verified emission reductions are repeated regularly and are thus to be considered as a cycle.
Retirement of verified emission reductions (9)
Once a verified emission reduction is used, it must be retired. This process is also reflected in the relevant registry. If the financing of a climate project is done via ClimatePartner, the verified emission reductions are bundled in a system certified by TÜV Austria and are then retired on a regular basis. This ensures that each verified emission reduction can no longer be sold and is only used once, thus preventing double counting.